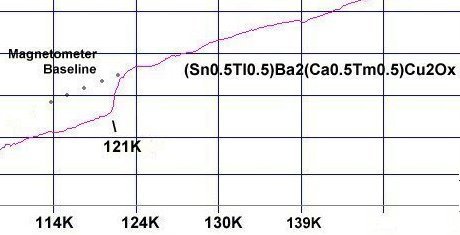
Magnetic susceptibility-vs-temperature graph of new 1212 superconductor.

Superconductors.ORG reports the discovery of [another] new high-temperature superconductor through the positioning of calcium and thulium in alternating CuO2 planes of a heavy-metal oxocuprate. Meissner-like behavior is observed in the compound (Sn0.5Tl0.5)Ba2(Ca0.5Tm0.5)Cu2Ox at temperatures near 120 Kelvin, suggesting the Ca-Tm synergy, already confirmed in a 3212 material, also applies to the 1212 structure type.

As can be seen in the above graphic, the 1212 and 3212 structures are identical except for the insulating layers. This similarity was the impetus behind efforts to translate success with Ca-Tm from a 3212 over to a 1212 structure.
At 115 Kelvin (the resistive Tc) (Sn0.5Tl0.5)Ba2(Ca0.5Tm0.5)Cu2Ox has a critical transition temperature more than 13 degrees higher than its closest analog (Pb0.5Tl0.5)Sr2(Ca0.8Y0.2)Cu2O7+.(1) This boost in Tc is believed due to the Ca/Tm ratio being exactly 1:1. This places disparate weight in alternating CuO2 planes, creating a unit cell that is effectively twice as large.
Verification that the observed Tc is coming from the target stoichiometry was accomplished by varying the Sn/Tl ratio. Even a slight variation (0.1 atom) suppressed the superconductive state.
This discovery may have ramifications beyond the pairing of just calcium and thulium. It suggests there may be other undiscovered HTSC copper-oxides that can be fashioned or improved by adjusting the weight ratios of alternating CuO2 planes.
Synthesis of the material was by the solid state reaction method. Stoichiometric amounts of the below precursors were mixed, pelletized and sintered in quartz tubing (gold foil was not available) for 36 hours at 850C. The pellet was then annealed for 10 hours at 500C in flowing O2.
Tm2O3 99.99% (Stanford Materials)RESEARCH NOTE: As with Sn-3212-Tm, this compound has been found to be strongly hygroscopic. All tests should be performed immediately after annealing.
- E. Joe Eck
© 2005 Superconductors.ORG
Patent Pending. All rights reserved.
(1) Tc~102K per M.R. Presland and J.L. Tallon, Physica C, Issue 177, 1991 Page(s): 1-7
 BACK to "News" page at Superconductors.ORG
BACK to "News" page at Superconductors.ORG